- Back en to Summary
11 Criticism on climate policy
John Stewart Coleman |
Founder of The Weather Channel, Chief Meteorologist of KUSI-TV in San Diego |
|---|
Mit folgendem Link wird von anderen Webseiten auf diese Seite verwiesen.
|
John Stewart Coleman *1934-10-15 †2018-01-20 |
Founder of The Weather Channel, Chief Meteorologist of KUSI-TV in San Diego ▶John Stewart Coleman: Who is who (Skeptiker) ▶John Stewart Coleman: Video (Präsentationen) |
2014
-
9th International Conference on Climate Change 2014
2014-07-08 en John Coleman Keynote - ICCC9 July 8, 2014
John Coleman Keynote - ICCC9 July 8, 2014
2011
-
John Coleman
2011-04-29 en Global Warming: Meltdown (Parts 1-9)
Global Warming: Meltdown (Parts 1-9)
This portion of the program quickly recaps my skeptical position about carbon dioxide being a significant green house warming gas in our atmosphere.
2009
2008
-
2008-03-20 en
 Founder of The Weather Channel Slams Global Warming!
Founder of The Weather Channel Slams Global Warming!
-
2008-11-12 en
 Al Gore sued for fraud: Global Warming is not man-made
Al Gore sued for fraud: Global Warming is not man-made
Global warming is not caused by humans. The hysteria about global warming is one big fraud. Learn more at these sites.
- KUSI News San Diego en John Coleman
The future of our civilization lies in the balance.
-
It is shocking, but true, to learn that the entire Global Warming
frenzy is based on the environmentalist's attack on fossil fuels,
particularly gasoline. All this big time science, international
meetings, thick research papers, dire threats for the future; all
of it, comes down to their claim that the carbon dioxide in the exhaust
from your car and in the smoke stacks from our power plants is
destroying the climate of planet Earth. What an amazing fraud;
what a scam.
According to Mr. Gore the polar ice caps will collapse and melt and sea levels will rise 20 feet inundating the coastal cities making 100 million of us refugees. Vice President Gore tells us numerous Pacific islands will be totally submerged and uninhabitable. He tells us global warming will disrupt the circulation of the ocean waters, dramatically changing climates, throwing the world food supply into chaos. He tells us global warming will turn hurricanes into super storms, produce droughts, wipe out the polar bears and result in bleaching of coral reefs. He tells us tropical diseases will spread to mid latitudes and heat waves will kill tens of thousands. He preaches to us that we must change our lives and eliminate fossil fuels or face the dire consequences.
With a preacher's zeal, Mr. Gore sets out to strike terror into us and our children and make us feel we are all complicit in the potential demise of the planet.
Here is my rebuttal
-
There is no significant man made global warming.
There has not been any in the past, there is none now and there is no
reason to fear any in the future. The climate of Earth is changing.
It has always changed. But mankind's activities have not overwhelmed or
significantly modified the natural forces.
Through all history, Earth has shifted between two basic climate regimes: ice ages and what paleoclimatologists call "Interglacial periods". For the past 10 thousand years the Earth has been in an interglacial period. That might well be called nature's global warming because what happens during an interglacial period is the Earth warms up, the glaciers melt and life flourishes. Clearly from our point of view, an interglacial period is greatly preferred to the deadly rigors of an ice age. Mr. Gore and his crowd would have us believe that the activities of man have overwhelmed nature during this interglacial period and are producing an unprecedented, out of control warming.
Well, it is simply not happening. Worldwide there was a significant natural warming trend in the 1980's and 1990's as a Solar cycle peaked with lots of sunspots and solar flares. That ended in 1998 and now the Sun has gone quiet with fewer and fewer Sun spots, and the global temperatures have gone into decline. Earth has cooled for almost ten straight years. So, I ask Al Gore, where's the global warming?
The cooling trend is so strong that recently the head of the United Nation's Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change had to acknowledge it. He speculated that nature has temporarily overwhelmed mankind's warming and it may be ten years or so before the warming returns. Oh, really. We are supposed to be in a panic about man-made global warming and the whole thing takes a ten year break because of the lack of Sun spots. If this weren't so serious, it would be laughable.
I love this civilization. I want to do my part to protect it.
- If Al Gore and his global warming scare dictates the future policy of our governments, the current economic downturn could indeed become a recession, drift into a depression and our modern civilization could fall into an abyss. And it would largely be a direct result of the global warming frenzy.
- Watts Up With That? (Antony Watts) en Weather Channel Founder Makes Another Challenge to Gore
-
Watts Up With That? (Antony Watts)
2008-05-05 en An open letter to environmentalists
- Pensée unique fr John Coleman
Dr. William Gray and Bill Clinton with Al Gore as Vice President
-
In a September, 2005, article from Discovery Magazine,
Dr. William Gray, now an emeritus professor of atmospheric
science at Colorado State University and a former president
of the American Meteorological Association, was asked if funding
problems that he was experiencing and has been experiencing could
be traced to his skepticism of man-made global warming. His response:
"I had NOAA money for 30 years, and then when the Clinton administration came in and Gore started directing some of the environmental stuff, I was cut off. I couldn't get any money from NOAA. They turned down 13 straight proposals from me."
This man is one of the most prominent hurricane experts in the world, cut off during the Clinton-Gore administration because he had been skeptical of global warming.
William Harper and Bill Clinton with Al Gore as Vice President
-
In fact, Al Gore's first act as Vice President was to
insist that William Harper be fired as the Chief Scientist at
the Department of Energy. Now, why was that?
Well, that's because William Harper had uttered words indicating that he was open minded to the issue of global warming. So off with his head.
They didn't want someone who was open minded. They wanted someone who was going to provide grants based on people who would verify this man-made global warming theory. Now, that was 1993 when Mr. Harper was relieved, the first year of the Clinton-Gore administration.
So for over a decade, all we got was a drumbeat of one-sided research, setting the stage for the false claim that there is a scientific consensus about whether or not man-made global warming is real.
Labelling as Stalinist
-
I remember Al Gore labeling me a Stalinist because when I
chaired the subcommittee on Research and Science Education,
I insisted that both sides be presented.
There was a study on research and the environment, a subcommittee of the Science Committee. And I insisted when I was chairman of the committee that expert witnesses on both sides be present at hearings and that they address each other's contentions. Well, to him, that is Stalinism.
Well, I would suggest that the propaganda campaign of the manmade global warming alarmists has far more in common with Stalinism than does insisting that both sides of an argument be heard.
There is a big problem
-
Unfortunately, for all those scientists who went along with the
scheme, now, over a decade later, there is a big problem.
Contrary to what all those scientists living on their Federal research grants predicted, the world hasn't been getting warmer.
In fact, for the last 7 years, there has been no warming at all, which has been verified even by, for example, Michel Jarraud of the World Meteorological Organization. He's their Secretary General.
He reluctantly admitted that global temperatures have not risen since 1998, according to a BBC article.
Global snowfall is at record levels and there are fewer, not more, hurricanes.
Conclusions
-
What we need to do is make sure that we develop clean energy
sources, not because of global warming but because of the health
of our children. And also, we need to be independent of foreign sources.
The fact is that foreign sources of oil, because we are not developing
our own oil resources as a result of the dynamics created by the global
warming juggernaut that we have been experiencing, the fact is that
we have not drilled for our own oil.
We have not focused on real alternatives to energy like nuclear energy. The fact is that we need to make sure right now that we do our very best not to be captured by this, what I consider to be one of the greatest hoaxes that I have seen in my lifetime, but instead focus our efforts on accomplishing something that is real and positive for the people of the world and the people of the United States of America.
We should be drilling for oil so that the terrorists overseas are denied the revenue when we are forced to buy oil from countries that are allied with these terrorists.
We need to make sure that we develop better engines, and make sure that those engines are not putting pollutants into the air and forget about the CO2, go to the pollutants.
Quellen / Sources:
-
Watts UP With That? (Anthony Watts)
2008-06-05 en Regarding the Lieberman-Warner Debate, Rep. Rohrabacher: "Do you really think the world is filled with morons?"From the Congressional Record, this speech was given on the floor of the U.S. House of Representatives. It is worth reading and posting elsewhere.
Lieberman-Warner Debate: Congressman Rohrabacher's Floor Speech on Global Warming
-
Dana Rohrabacher
2008-05-14 en Congressman Rohrabacher's Floor Speech on Global Warming (Wayback‑Archiv)MAN-MADE GLOBAL WARMING
House of Representatives - May 14, 2008
12 Climate impacts
13 Climate in the past
- a)
de
Die Mittelalterliche Warmzeit und die Kleine Eiszeit
en Medieval Warm Period and the Little Ice Age
fr L'optimum climatique médiéval et le petit âge glaciaire - b)
de
Die Mittelalterliche Warmzeit (ca. 900 - 1350)
en The Medieval Warm Period
fr L'optimum climatique médiéval - c)
de
Die Kleine Eiszeit (von 1350 bis ca. 1850)
en The Little Ice Age
fr Le petit âge glaciaire - d)
de
Einfluss der Sonne auf die Mittelalterliche Wärmeperiode und Kleine Eiszeit
en Solar inpact on the Medieval Climate Anomaly and the Little Ice Age
fr Impacte du soleit sur L'optimum climatique médiéval et le petit âge glaciaire - e)
de
IPCC liess das Mittelalterliche Klimaoptimum und die Kleine Eiszeit
verschwinden
en IPCC changed viewpoint on the MWP in 2001
fr Le GIEC fait disparaître l'optimum climatique médiéval - f)
de
1815 1815 Der Ausbruch des Vulkans Tambora
1816 Das Jahr ohne Sommer
↑
a) Die Mittelalterliche Warmzeit und die Kleine Eiszeit
en Medieval Warm Period and the Little Ice Age
fr L'optimum climatique médiéval et le petit âge glaciaire
-
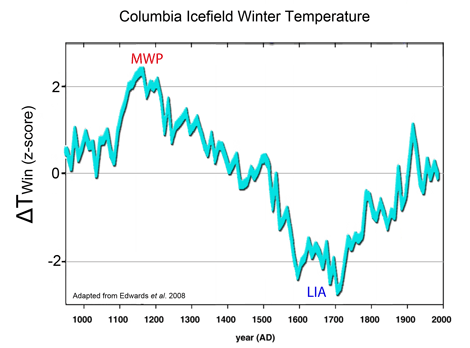
In der mittelalterlichen Warmperiode waren die Temperaturen im Mittel 2 - 4°C höher als heute,
Island und Grönland wurden im 9. Jahrhundert durch die Wikinger besiedelt;
das Packeis zog sich weiter nördlich zurück;
in England und Grönland wurde Wein angebaut;
in Island wuchsen Eichen und man baute Weizen und Gerste an;
die Nordwestpassage und Nordostpassage war schiffbar.
![]()
![]()
The last thousand years Climate changes in Europe

-
Climate Change Science en
The last thousand years in Europe
-
Klimanews
2008-09-30 de Mittelalterliche Warmzeit und Kleine Eiszeit in der Antarktis, im Widerspruch zum Michael Mann Hockeystick
-
Paul Homewood
2011-11-01 de What Was Life Like In The Little Ice Age? - Part I
2017-02-06 de
![]() Kathedralen - Superbauten im Mittelalter
Kathedralen - Superbauten im Mittelalter
Die Dokumentation erzählt die Geschichte des Kathedralenbaus und zeigt die dramatischen Momente im 1000-jährigen Leben des Doms.
-
Wikiwand
de Mittelalterliche WarmzeitIn der Zeitspanne, in der die mittelalterliche Warmperiode verortet wurde, kam es in Europa zu einer regelrechten Bevölkerungsexplosion.
Dieses ist sicherlich auch auf die günstige Klimaentwicklung zurückzuführen, aber keineswegs ausschließlich.
Zwar kam es infolge des wärmeren Klimas in Europa zu einer Expansion der Agrarwirtschaft, der Getreideanbau war nun sowohl in wesentlich nördlicheren als auch in höher gelegenen Gebieten möglich.
So wurde Getreidewirtschaft bis nach Norwegen und in den Bergen Schottlands nachgewiesen, die in der nachfolgenden Kleinen Eiszeit und der damit verbundenen Abkühlung des Klimas wieder eingestellt wurde.
So wird angenommen, dass sich die Bevölkerung in Europa zwischen 1100 und 1400 fast verdreifacht hat.
| de |
▶ Internet-Terror: Manipulation von Wikipedia durch einen Administrator ▶ Das Lexikon der Lügen ▶ Vom Onlinelexikon zur Propagandamaschine: Zensur, Einschüchterung und arglistige Täuschung ▶ Wikipedia: Klima-Fälscher Connolley: Der Mann, der unser Weltbild umschrieb ▶Die dunkle Seite von WIKIPEDIA: EIKE Zensur - kurz und knapp [Who is who (Skeptische Institute): EIKE; Wikipedia: Websites, Opfer: EIKE, Manipulatoren: Andol] |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| en |
▶ At Wikipedia, one man engineers the debate on global warmingator |
|||||
| fr |
▶ A Wikipedia, un homme dirige le débat sur le réchauffement climatique et à sa manière |
-
Medieval Warming Period
A look back to the Medieval Warming Period offers an insight into how things changed in the following centuries.
Most people are aware that the Vikings colonised and farmed parts of Greenland in ways that are still to this day not possible.
In Europe summer temperatures were between 0.7C and 1.0C warmer than 20th Century averages.
Central European summers were even warmer, as much as 1.4C warmer than now.
During the height of the Warm Period, so many lords quaffed prime English wines that the French tried to negotiate trade agreements to exclude them from the Continent.
Populations rose sharply during medieval times.
Numerous examples are quoted which show how crops were grown at altitudes where crops cannot be supported today such as Dartmoor and the Pennine Moors.
In Scandinavia farming spread 100 to 200 meters farther up valleys and hillsides in central Norway, from levels that had been static for more than 1000 years.
To the south in the Alps, tree levels rose sharply and farmers planted deeper and deeper into the mountains. During late prehistoric times, numerous copper mines had flourished in the Alps until advancing ice sealed them off; late medieval miners reopened some of these when the ice retreated.
For five centuries, Europe basked in warm, settled weather, with only the occasional bitter winters, cool summers and memorable storms.
Summer after summer passed with long, dreamy days, golden sunlight and bountiful harvests.
Compared with what was to follow, these centuries were a climatic golden age.
Greenland
Eirik the Red is credited with discovering Greenland in the 10th Century and Viking colonists followed him to set up farming settlements as far north as Godthab.
They found the green summer pastures were better than either back home in Norway or Iceland.
However in the 13th Century Greenland and Iceland experienced increasing cold.
Sea ice spread south creating difficulties for Norse ships sailing from Iceland as early as 1203.
By 1250 many fewer ships made the crossing to Greenland and those that did had to take a more hazardous route further south in the open Atlantic to avoid pack ice off southeastern Greenland.
Extent of the Little Ice Age
There is been plenty of historical evidence which confirms the existence of a much colder climate in much of Europe between the 14th and 19th Centuries.
This is not surprising because there is such a wealth of historical records and documents which has been handed down from the Europe of those days.
Glaciers
We tend to regard alpine landscapes today such as those in Switzerland as being picturesque and think that the people there live in an beautiful idyll.
It was not always so.
In the 16th Century the occasional traveller would remark on the poverty and suffering of those who lived on the marginal lands in the glacier's shadow.
-
Watts Up With That? (Antony Watts)
2011-11-11 en "Without energy, life is brutal and short"Storms and Floods It was not only the cold that was a problem during the Little Ice Age.Throughout Europe, the years 1560-1600 were cooler and stormier, with late wine harvests and considerably stronger winds than those of the 20th Century. Storm activity increased by 85% in the second half of the 16th Century and the incidence of severe storms rose by 400%.
Perhaps the most infamous of these storms was the All Saints Flood in November 1570, which worked its way northeast up the North Sea.The storm brought enormous sea surges ashore in the Low Countries, flooding most of Rotterdam, Amsterdam, Dordrecht and other cities and drowning at least 100,000 people. In the River Ems further north in Germany, sea levels rose an incredible four and a half meters above normal.
In 1607 another storm caused even greater floods in the Bristol Channel with flood waters rising 8 meters above sea level miles inland.
Later in the 17th Century, great storms blew millions of tonnes of formerly stable dunes across the Brecklands of Norfolk and Suffolk, burying valuable farm land under meters of sand. This area has never recovered and is heathland. A similar event occurred in Scotland in 1694. The 1400 hectare Culbin Estate had been a prosperous farm complex next to the Moray Firth until it was hit by another huge storm which blew so much sand over it that the farm buildings themselves disappeared. A rich estate had become a desert overnight and the owner, the local Laird, died pauper three years later.
The Great Storm of 1703 is recognized as the most powerful storm ever recorded in England and caused immense damage there as well as across the North Sea in Holland and Denmark.
Cold, Snow and Ice
Between 1680 and 1730, the coldest cycle of the Little Ice Age, temperatures plummeted and the growing season in England was about five weeks shorter than now. The winter of 1683/4 was so cold that the ground froze to a depth of more than a meter in parts of south west England and belts of ice appeared off the Channel coast of England and northern France. The ice lay up to 30 miles offshore along the Dutch coast and many harbours were so choked with ice that shipping halted throughout the North Sea.
Another exceptional winter was that of 1708/9. Deep snow fell in England and lasted for weeks while further East people walked from Denmark to Sweden on the ice as shipping was again halted in the North Sea. Hard frosts killed thousands of trees in France, where Provence lost most of its orange trees and vineyards were abandoned in northern France, not to be recultivated until the 20th Century. In 1716 the Thames froze so deep that a spring tide raised the ice fair on the river by 4 meters! The summer of 1725 in London was the coldest in the known temperature record and described as "more like winter than summer".
Fishing and Sea Conditions
During the 17th Century conditions around Iceland became exceptionally severe. Sea ice often blocked the Denmark Strait throughout the summer. In 1695, ice surrounded the entire coast of Iceland for much of the year, halting all ship traffic. The inshore cod fishery failed completely, partly because the fish may have moved offshore into slightly warmer water. On several occasions between 1695 and 1728, inhabitants of the Orkney Islands were startled to see an Inuit in his kayak paddling off their coasts. These solitary hunters must have spent weeks marooned on large ice floes. As late as 1756, sea ice surrounded much of Iceland for as many as thirty weeks a year.
The cod fishery off the Faeroe Islands failed completely as the sea surface temperature became 5C cooler than today, while enormous herring shoals deserted Norwegian waters for warmer seas further south.
Famine
As climatic conditions deteriorated, a lethal mix of misfortunes descended on a growing European population. Crops failed and cattle perished by diseases caused by abnormal weather. Famine followed famine bringing epidemics in their train, bread riots and general disorder. Witchcraft accusations soared, as people accused their neighbours of fabricating bad weather.
Farming was just as difficult in the fledgling European colonies of North America where there were several severe drought cycles between 1560 and 1612 along the Carolina and Virginia coasts.
From 1687 to 1692, cold winters and cool summers led to a series of bad harvests. Alpine villagers lived on bread made from ground nutshells, whilst in France, wine harvests were delayed till as late as November. Widespread blight damaged many crops, bringing one of the worst famines in Europe since 1315. Finland lost perhaps as much as a third of its population to famine and disease in 1696-7.
Things did not improve. 1739 brought more problems, ruining grain and wine harvests over much of western Europe, while winter grain yields were well down because the ground was too hard to plough for weeks.
By 1815, Europe was struggling with yet another cold spell, when the Tambora eruption made matters a whole lot worse. The following year was described as "The year without a summer". In France the grain harvest was half its normal level and southern Germany suffered a complete harvest failure. In Switzerland grain and potato prices tripled, and 30000 were breadless, without work and resorted to eating "sorrel,moss and cats".
Inevitably such suffering brought with it social unrest, pillaging, rioting and criminal violence. The famine encouraged many to emigrate to America, although in Saint John's, Newfoundland, 900 were sent back to Europe because there was so little food in town.
The crisis of 1816/7 was the last truly extensive food dearth in the Western world and its effects ranged from the Ottoman Empire, to parts of North Africa, large areas of Switzerland and Italy, western Europe and even New England and Canada. Other parts of the world were also badly affected such as China. Death tolls are hard to calculate but 65000 may have perished in Ireland, while in Switzerland the death rate could have doubled. The death toll would have been much worse in England and France but for the availability of and ability to efficiently distribute reserve stocks of food.
| Craig Loehle |
Ph.D., Principal Scientist with the National Council for Air and Stream
Improvement (NCASI) His research interests include ecological modeling, landscape ecology, life history theory, and natural resource management. He is the author of over 100 scientific publications. ▶Craig Loehle: Who is who (Skeptiker) |
![]() de
de
![]() en
en
![]()
Annual mean temperature reconstruction for Greenland (blue line)
calibrated to instrumental temperatures for the west coast of Grennland
(red line) with 2 standard deviation error bars (grey shading).

-
Klimaskeptiker Info
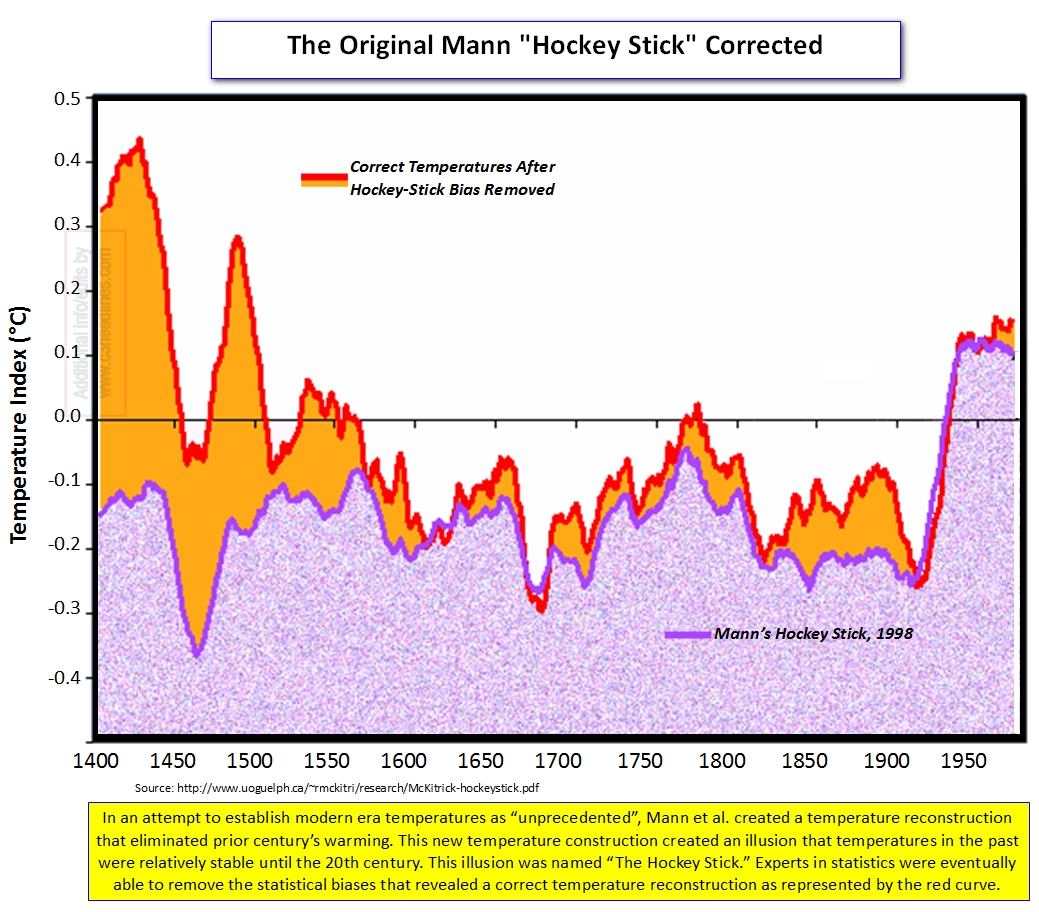
2010-11-24 de Ein regionaler Ansatz bei der Untersuchung des Mittelalterlichen Klimaoptimumes und der Kleinen EiszeitZu den wichtigsten Ikonen der Vertreter der angeblichen anthropogenen globalen Erwärmung (AGW) gehört die berühmt-berüchtigte Hockeystick-Graphik von Michael Mann et al., mit denen auch Al Gore der Weltöffentlichkeit einreden wollte, die Erwärmung am Ende des 20. Jahrhunderts sei in den letzten 1000 Jahren beispiellos gewesen.
Das historisch gut belegte Mittelalterliche Klimaoptimum um das Jahr 1000 wurde von den Alarmisten dabei ebenso negiert wie die Kleine Eiszeit zwischen 1650 und 1850.
Eine weitere Studie tritt dieser falschen Darstellung der Klimageschichte entgegen.
-
Watts Up With That? (Antony Watts)
2010-11-24 en A regional approach to the medieval warm period and the little ice age
-
Fredrik Charpentier Ljungqvist, Stockholm University Sweden
en A regional approach to the medieval warm period and the little ice age
A regional approach to the medieval warm period and the little ice age
-
C3 Headlines Climate Cycles Change
en Historical Temperatures - Charts/Graphs
|
The Original Mann "Hockey Stick" Corrected |
Fabricating the 'Blade' of the 'Hockey-Stick' |
|
|

|
↑
b) Die Mittelalterliche Warmzeit (ca. 900 - 1350)
en Medieval Warm Period (or Medieval Climate Optimum)
fr L'optimum climatique médiéval
- de Allgemein en General fr Généarale
-
de
Die Mittelalterliche Warmzeit - Erwärmung oder Datenmanipulation?
en The Medieval Warm Period - warming, or data manipulation? - de Mittelalterliche Wärmeperiode war um ein halbes Grad wärmer als heute
-
de
Die Wikinger in Grönland
en The Vikings in Greenland
fr Les Vikings en Grœnland -
de
Umfahrung Grönlands und des sibirischen Nordmeers 1421-1423
en The Voyages of the Treasure Fleets 1421-1423
fr Le voyage de l'armade chinoise 1421-1423 - de Kartographie der Mittelalterlichen Wärmeperiode
-
de
Die Mittelalterliche Warmzeit bei den Inkas in Peru
en The Medieval Warm Period linked to the success of Machu Picchu, Inca Empire
fr L'optimum climatique médiéval au Pérou - de The pre Columbian Civilisations of Central America - The Mesoamericans
- de Die Mittelalterliche Wärmeperiode in Afrika
- de Die Mittelalterliche Wärmeperiode in der Antarktis
-
de
Belege für mittelalterliches Klimaoptimum im Westen der USA
en Giant Sequoias Yield Longest Fire History from Tree Rings - de Die Mittelalterliche Wärmeperiode der kanadischen Baffininsel
- en Evidence of the Medieval Warm Period in Australia, New Zealand and Oceania
- de Klimamodelle können nicht erklären, warum es vor 800 Jahren wärmer war
←
Allgemein
en General
fr Générale
-
de
Die Mittelalterliche Warmzeit (auch Mittelalterliches Klimaoptimum
genannt) war eine vom 9. bis in das 14. Jahrhundert andauernde
Periode vergleichsweise milden Klimas.
Sie folgte auf das kalte Pessimum der Völkerwanderungszeit und endete mit Beginn der sog. "Kleinen Eiszeit".
-
en
The Medieval Warm Period (MWP) or Medieval Climate Optimum was a
time of unusually warm climate in the North Atlantic region,
lasting from about the tenth century to about the fourteenth century.
The Medieval Warm Period was a time of warm weather around 800-1300 AD during the European Medieval period.
-
fr
L'optimum climatique médiéval parfois appelé réchauffement
climatique de l'an mil est une période de climat inhabituellement
chaud localisé sur les régions de l'Atlantique nord et ayant duré
du Xe siècle jusqu'au XIVe siècle approximativement.
L'optimum climatique médiéval est une période de réchauffement climatique s'étalant environ de 800 à 1300 après Jésus-Christ, durant le Moyen Âge européen.
-
Wikipedia de
Mittelalterliche Warmzeit
en Medieval Warm Period (or Medieval Climate Optimum)
fr Optimum climatique médiéval
-
EIKE Europäisches Institut fü Klima und Energie Jena
2009-04-22 de Mittelalterliches Optimum, lokal oder global ? "Spectrum der Wissenschaft" unterschlägt außereuropäische Berichte über die Mittelalterliche Warmzeit!
←
Die Mittelalterliche Warmzeit - Erwärmung oder Datenmanipulation?
en
The Medieval Warm Period - warming, or data manipulation?
![]() Click for an interactive graphic that will expand each graph on mouseover
Click for an interactive graphic that will expand each graph on mouseover

-
Watts Up With That? (Antony Watts)
2009-11-29 en The Medieval Warm Period - a global phenomenon, unprecedented warming, or unprecedented data manipulation?
← Mittelalterliche Wärmeperiode war um ein halbes Grad wärmer als heute
-
Die kalte Sonne (Fritz Vahrenholt & Sebastian Lüning)
2015-06-09 de Zweiter Klimazustandsbericht zum Ostseeraum: Mittelalterliche Wärmeperiode war um ein halbes Grad wärmer als heuteMitte Mai 2015 erschien der Zweite Klimazustandsbericht zum Ostseeraum, koordiniert vom Helmholtz-Zentrum Geesthacht.
Das vorindustrielle Klima im Ostseeraum war alles andere als stabil.
Im Zeitraum 8000-4500 Jahre vor heute war es laut Studie um ein bis dreieinhalb Grad wärmer als heute.
Dies entspricht dem sogenannten "mittelholozänen Klimaoptimum".
Eine Hitzeperiode, die in der Öffentlichkeit heute gänzlich unbekannt ist und auch von den Pressestellen offenbar nicht sehr geliebt wird.
Plötzlich stellt sich die Zwischenüberschrift "Erwärmung schreitet voran" in einem ganz anderen Licht dar.
Es wird derzeit wärmer - aber es ist noch lange nicht wieder so warm wie vor 8000-4500 Jahren.
Am Ende der Kurzfassung wird auf die Mittelalterliche Wärmeperiode übergeleitet, die Teil des Folgekapitels von Tadeusz Niedzwiedz und Kollegen ist.
Im Text der Darstellung über das letzte Jahrtausend findet sich die altbekannte Klimazyklik, die man zwischenzeitlich beim IPCC unter den Tisch fallen lassen wollte:
Mittelalterliche Wärmeperiode, Kleine Eiszeit, Moderne Wärmeperiode:
Ein klares Statement:
Zur Zeit der Mittelalterlichen Wärmeperiode war es durchschnittlich um ein halbes Grad wärmer als heute.
Auch diesen nicht ganz unwichtigen Umstand wollte man keinesfalls in der Pressemitteilung zum Bericht erwähnt sehen.
Wie konnte es vor 1000 Jahren wärmer als heute sein, obwohl doch der CO2-Gehalt der Atmosphäre außerordentlich niedrig war?
Quellen / Sources:
-
Springer Link
2015-04-04 en Climate Change During the Holocene (Past 12,000 Years)
-
Springer Link
2015-04-04 en The Historical Time Frame (Past 1000 Years)
←
Die Wikinger in Grönland
en The Vikings in Greenland
fr Les Vikings en Grœnland
de Allgemein en General fr Générale
de Verzeichnis en Contents fr Sommaire
- 2019
- en Study shows that Vikings enjoyed a warmer Greenland
- 2011
- en
Warum die Wikinger aus Grönland flohen
Ende des 14. Jahrhunderts zogen sie sich zurück - 2010
- en
Changing Greenland: Viking Weather
In 982 Erik the Redhe landed along a fjord near Qaqortoq
de Text en Text fr Texte
⇧ 2019
↑ en Study shows that Vikings enjoyed a warmer Greenland
-
Watts UP With That? (Antony Watts)
2019-02-19 en Study shows that Vikings enjoyed a warmer GreenlandStudy shows that Vikings enjoyed a warmer Greenland

 This is a 21st-century reproduction of Thjodhild's church on Erik
the Red's estate (known as Brattahlíð) in present day Qassiarsuk,
Greenland
This is a 21st-century reproduction of Thjodhild's church on Erik
the Red's estate (known as Brattahlíð) in present day Qassiarsuk,
Greenland
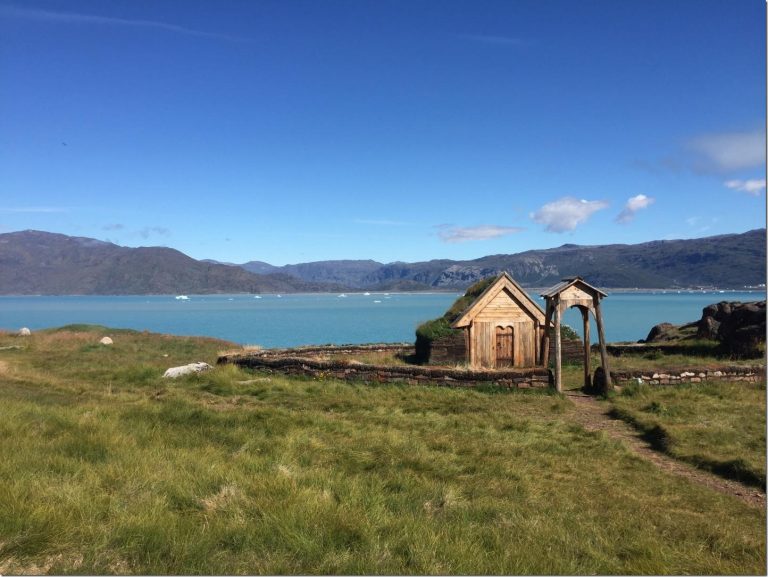

After reconstructing southern Greenland's climate record over the past 3,000 years, a Northwestern University team found that it was relatively warm when the Norse lived there between 985 and 1450 C.E., compared to the previous and following centuries.
"People have speculated that the Norse settled in Greenland during an unusually, fortuitously warm period, but there weren't any detailed local temperature reconstructions that fully confirmed that.
And some recent work suggested that the opposite was true," said Northwestern's Yarrow Axford, the study's senior author.
"So this has been a bit of a climate mystery."
Overall, the climate was about 1.5-degrees Celsius warmer than the surrounding cooling centuries.
This warmer period was similar to southern Greenland's temperatures today, which hover around 10-degrees Celsius (50-degrees Fahrenheit) in summer.
⇧ 2011
↑ Warum die Wikinger aus Grönland flohen
Ende des 14. Jahrhunderts zogen sie sich zurück
-
Spiegel Online
2011-05-31 de Warum die Wikinger aus Grönland flohenLange lebten die Wikinger in Grönland.
Als die Nordmänner ihre Kette kleiner Kolonien entlang der Westküste und im Süden der Insel errichteten, herrschte relativ mildes Klima, vergleichbar mit den heutigen Gegebenheiten.
In diesem "Mittelalterlichen Klimaoptimum" grünte selbst Grönland - daher der Name der Insel.
Als die Durchschnitts-Temperaturen später sanken, versuchten die Wikinger diesem Klima zunächst zu trotzen, mussten aber schließlich aufgeben.
⇧ 2010
↑ en Changing Greenland: Viking Weather
In 982 Erik the Redhe landed along a fjord near Qaqortoq
-
National Geographic
2010-06 en Changing Greenland: Viking WeatherGreenland's first experience of hype happened a millennium ago when Erik the Red arrived from Iceland with a small party of Norsemen, aka Vikings.
Erik was on the lam (from the Old Norse word lemja) for killing a man who had refused to return some borrowed bedsteads.
In 982 he landed along a fjord near Qaqortoq, and then, despite the bedsteads incident, he returned to Iceland to spread word about the country he had found, which, according to the Saga of Erik the Red, "he called Greenland, as he said people would be attracted there if it had a favorable name."
Erik's bald-faced marketing worked. Some 4,000 Norse eventually settled in Greenland.
The Vikings, notwithstanding their reputation for ferocity, were essentially farmers who did a bit of pillaging, plundering, and New World discovering on the side.
Along the sheltered fjords of southern and western Greenland, they raised sheep and some cattle, which is what farmers in Greenland do today along the very same fjords.
They built churches and hundreds of farms; they traded sealskins and walrus ivory for timber and iron from Europe.
Erik's son Leif set out from a farm about 35 miles northeast of Qaqortoq and discovered North America sometime around 1000.
In Greenland the Norse settlements held on for more than four centuries.
Then, abruptly, they vanished.
-
National Geographic Photo Gallery
2010-06 en Viking Weather - The Changing Face of GreenlandAs Greenland returns to the warm climate that allowed Vikings to colonize it in the Middle Ages, its isolated and dependent people dream of greener fields and pastures - and also of oil from ice-free waters.
←
Umfahrung Grönlands und des sibirischen Nordmeers 1421-1423
en The Voyages of the Treasure Fleets 1421-1423
fr Le voyage de l'armade chinoise 1421-1423
▷Klimaänderungen der Vergangenheit (Wayback ohne Bilder)
Der Wasserplanet war im Original auf dem Server von ZUM gespeichert.
Die Dateien wurden von Lehrern des ZUM entfernt,
die Dateinamen wurden belassen
(damit auch gleich Propaganda für ZUM gemacht werden kann)
Die Links führen heute nur noch auf die Homepage
von ZUM
auf denen nur noch der Mensch für den Klimawandel verantwortlich
gemacht wird.
Alle Hinweise auf natürliche Ursachen des
Klimawandels wurden gelöscht
(vom Server entfernt).
![]() Animation
Animation
![]() Wasserplanet
Wasserplanet
![]()
Umfahrung Grönlands und des sibirischen Nordmeers 1421-1423
Animation: Auf das Bild klicken / Click on the image
(Datei gelöscht - Im Wayback‑Archiv nicht gespeichert)
Wasserplanet
de
1421: Umfahrung Grönlands und des sibirischen Nordmeers
Eine solche Nordpassage ist heute nicht mehr möglich.
1421.tv
en
1421 - The Year China discovered the World
Voyages of the Treasure Fleets, 1421-1423
The Voyages of the Treasure Fleets, 1421-3 are illustrated here using an animated flash movie. Once loaded you can view the passage of the fleets using the play button.
de Chinesische Website mit Animation
-
Am 8. März 1421, begann eine der grössten Flotten der Welt mit
über 100 Schiffen, die teilweise mehr als 150 m lang waren ihre
Reise um die Welt. Kaiser Zhu Dis Admiral Zheng He und andere
sollten den Tribut der Barbaren nach China bringen und der Welt
die Religion des Konfuzius.
Dabei entdeckten Sie Jahrzehnte vor Kolumbus, Maggelan und Cook Amerika, Australien, und die Antarktis.
Nach 2 Jahren kehrten sie nach Umfahrung Grönlands und des sibirischen Nordmeers wieder nach China zurück.
Eine solche Nordpassage ist heute nicht mehr möglich.
1492: Seit 80 Jahren kein Bischof mehr wegen Eis Grönland
-
1492 stellte der Papst fest, dass seit 80 Jahren kein Bischof
mehr wegen Eis Grönland hätte besuchen können.
Seit damals waren die Siedler wegen der Kälte wohl nach Neufundland weiter gewandert oder ausgestorben.
Noch 1408 beschreiben Vermählungsurkunden der grössten grönländischen Grundbesitzer aus staatl. Archiven in Oslo exakt die Landflächen, Viehbestände usw. ( z.B. grosse Schafs- und Rinderherden die auf saftigen Weiden grasten)
← Kartographie der Mittelalterlichen Wärmeperiode
-
Die kalte Sonne (Fritz Vahrenholt & Sebastian Lüning)
Das Projekt:
2015-11-07 de Kartographie der Mittelalterlichen Wärmeperiode: Online-Atlas einer noch immer unverstandenen Hitzephase
←
Mittelalterliche Warmzeit bei den Inkas in Peru
en The Medieval Warm Period linked to the success
of Machu Picchu, Inca Empire
fr L'optimum climatique médiéval au Pérou
|
Gemäss IPCC |
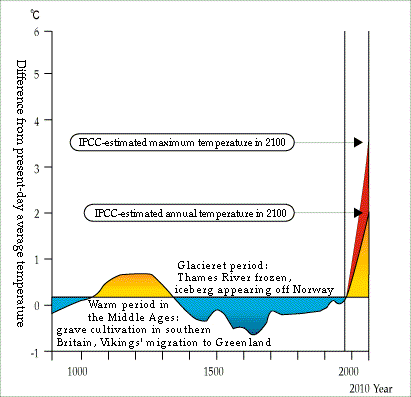
de Der IPCC-Bericht von 2001 unterschlägt die früheren Perioden, die wärmer waren als heute: "aktuelle Belege sprechen nicht für globale synchrone Perioden von anomaler Kälte oder Wärme während dieses Zeitrahmens, und die geläufigen Begriffe 'Kleine Eiszeit' und 'Mittelalterliches Klimaoptimum' scheinen nur geringen Wert zur Beschreibung hemisphärischer oder globaler Trends oder Veränderungen der Durchschnittstemperaturen in vergangenen Jahrhunderten zu haben.". en The 2001 IPCC report suppresses evidence of earlier periods warmer than today: "current evidence does not support globally synchronous periods of anomalous cold or warmth over this time frame, and the conventional terms of 'Little Ice Age' and 'Medieval Warm Period' appear to have limited utility in describing trends in hemispheric or global mean temperature changes in past centuries". fr Le rapport 2001 du GIEC escamote les périodes du passé plus chaudes qu'aujourd'hui |
Realität
en Reality
fr Réalité
de Die AGW-Anhänger haben die gut dokumentierten und starken Klimaschwankungen der letzten 1000 Jahre, die erheblich intensiver waren als die kurzfristige Erwärmung zwischen 1980 und 2000, als lokale europäische Phänomene kleinzureden versucht.
Dieser Versuch, Beweise gegen die CO2-Treibhaushypothese auszuhebeln, ist jetzt gescheitert.
-
Klimaskeptiker Info
2009-07-08 de Inkas blühten im mittelalterlichen Klimaoptimum auf
en Of course, there's many researchers, such as Michael Mann and his thoroughly discredited "hockey stick" that try mightily to make the Medieval Warm Period disappear.
The rapid expansion of the Inca from the Cuzco area of highland Peru produced the largest empire in the New World between ca. AD 1400-1532.
Although this meteoric rise may in part be due to the adoption of innovative societal strategies, supported by a large labour force and standing army, we argue that this would not have been possible without increased crop productivity, which was linked to more favourable climatic conditions.
-
Whatts Up With That? (Anthony Watts)
2009-07-08 en The Medieval Warm Period linked to the success of Machu Picchu, Inca Empire
-
A. J. Chepstow-Lusty, M. R. Frogley, B. S. Bauer, M. J. Leng,
K. P. Boessenkool, C. Carcaillet, A. A. Ali,
and A. Gioda
2009-03-04 en Putting the rise of the Inca Empire within a climatic and land
management context
Putting the rise of the Inca Empire within a climatic and land
management context
-
Living in Peru / Nicholas Asheshov
2009-07-01 en Opportunity knocks, again, in the Andes
-
Wikipedia de
Inka
en Inca Empire
fr Civilisation inca
← The pre Columbian Civilisations of South America
-
Climate History
en What Hubert Lamb Really Wrote About The Medieval Warm PeriodThe subject of the Medieval Warm Period is widely misunderstood.
Not least because few today have read the works of the historian and meteorologist who first brought awareness of climate and its impact on human history to wide public attention.Changes in climate together with extreme weather events have played major roles in the history of the pre-Columbian civilizations of Central and South America of the past two millennia, including the period known as the Medieval Warm Period.
en Drought and the Collapse of the Maya Civilisation
The fascination these abandoned cities hold arose because it became clear that many great cities, over a very wide area, had been abandoned before the arrival of the Spanish conquistadors. These cities and their magnificent buildings had clearly been centres of major states, supported by a vast complex of productive farms.
To name just some of the more significant cities:
Aguateca, Calakmul, Copan, Caracol, Chichen Itzan, Coba, Copan, Edzna, Ek Balem, El Mirador, Izimte, Palenque, Rio Azul, Tikal, Uaxactun, Uxmal & Yaxchilan.en The pre Columbian Civilisations of Central America - The Mesoamericans
There is a pre Conquest history of civilisations in Central America that extends back 3,500 years.
It's thought that humans have been in the Americas since 12,000 - 18,000 years BC.
The earliest human artefacts found so far are from Chile and date to around 11,000 BC.
By the 15th century AD most of the Americas were quite heavily populated.
In total the population of the Americas in pre Colombian times is estimated to have stood at around 40 million people - it may have been higher
en The pre Columbian Civilisations of South America
Mochica, Chimu, Sican, Wari, Tiwanaku and Inca ~ plus Amazonia
← Die Mittelalterliche Wärmeperiode in Afrika
-
Die kalte Sonne (Fritz Vahrenholt & Sebastian Lüning)
2015-11-23 de Die Mittelalterliche Wärmeperiode in Afrika
| de | en | fr |
|---|---|---|
|
Auswirkungen des Klimas Auswirkungen auf Afrika |
Impact of Climat Change Impacts on Africa |
Impacts du climat Impacts en Afrique |
← Die Mittelalterliche Wärmeperiode in der Antarktis
-
Die kalte Sonne (Fritz Vahrenholt & Sebastian Lüning)
2015-12-15 de Ganzen Kontinent mit einem Datenpunkt erklären? Antarktische Außenseiter-Studien zur Mittelalterliche Wärmeperiode offenbaren große LiteraturlückenErwärmung während der MWP
Peinlich: Alle anderen Arbeiten von der Antarktischen Halbinsel zeigen deutliche Hinweise auf eine Erwärmung während der MWP.
Die Amerikaner dokumentieren in ihrer Studie eine 200 Jahre andauernde Warmphase, die sich dort um das Jahr 1000 n. Chr. ereignete.
Im Sedimentkern findet sich in jenem Zeitabschnitt eine Lage, die reich an organischem Gehalt ist (siehe Abbildung unten).
Die Wärme führte zu einem Aufblühen der Lebewelt, deren Reste heute im Bohrkern enthalten sind.
Erwärmung ab 1600 n. Chr
Eine ungewöhnlich frühe Erwärmung ab 1600 n. Chr., die zur Modernen Wärmeperiode überführte.
Die Erwärmung begann mehrere hundert Jahre bevor der CO2-Gehalt der Atmosphäre im industrielen Zeitalter nach oben schnellte.
Dieser Wärmeepisode des 17. Jahrhunderts begegnen wir übrigens auch in einigen anderen Studien aus der Antarktis.
Dronning Maud Land in der Ostantarktis
Wichtige Erkenntnis: Von 1000 bis 1250 n. Chr.war es so warm wie heute.
Eisschelfs südlich des Weddell-Meeres
Insgesamt zeigt jedoch noch immer die allergrößte Anzahl der Studien in der Antarktis eine MWP-Erwärmung.
-
Die kalte Sonne (Fritz Vahrenholt & Sebastian Lüning)
2015-12-01 de Die Mittelalterliche Wärmeperiode in der Antarktis: Weshalb können die Klimamodelle sie nicht reproduzieren?
| de | en | fr |
|---|---|---|
|
Auswirkungen des Klimas Antarktis (Südpol) |
Effects of Climate Change Antarctic (South Pole) |
Conséquences climatiques Antarctique (Pôle Sud) |
←
Belege für mittelalterliches Klimaoptimum im Westen der USA
en
Giant Sequoias Yield Longest Fire History from Tree Rings
-
Klimaskeptiker Info
2010-03-17 de Belege für mittelalterliches Klimaoptimum im Westen der USADas in Europa historisch gut belegte mittelalterliche Klimaoptimum, während dessen es um das Jahr 1200 deutlich wärmer war als gegenwärtig, wollen die Anhänger der AGW-Hypothese als auf Europa begrenztes Phänomen marginalisieren.
Jetzt liefert eine Studie weitere Belege für den globalen Charakter der mittelalterlichen Warmzeit.
-
Klimaskeptiker Info
2010-03-17 en Giant Sequoias Yield Longest Fire History from Tree RingsCalifornia's western Sierra Nevada had more frequent fires between 800 and 1300 than at any time in the past 3,000 years, according to a new study led by Thomas W. Swetnam, director of UA's Laboratory of Tree-Ring Research.
← Die Mittelalterliche Wärmeperiode der kanadischen Baffininsel
-
Die kalte Sonne (Fritz Vahrenholt & Sebastian Lüning)
2016-01-16 de Eine Moräne macht noch keinen Winter: Mittelalterliche Wärmeperiode behauptet sich im Faktencheck gegen plumpes Aktivistenpaper zur kanadischen Baffininsel
-
Watts Up With That? (Antony Watts)
Sebastian Lüning
2016-01-18 en Baffin Island study disappoints: The illusive 'coup de grace' on the Medieval Warm Period
← en Evidence of the Medieval Warm Period in Australia, New Zealand and Oceania
-
Watts Up With That? (Antony Watts)
Sebastian Lüning
2016-01-09 en Evidence of the Medieval Warm Period in Australia, New Zealand and Oceania
← Klimamodelle können nicht erklären, warum es vor 800 Jahren wärmer war
-
Klimaskeptiker Info
2009-12-04 de Jo Nova findet das mittelalterliche Klimaoptimum
Eine der Kernbehauptungen der Klima-Alarmisten ist es, daß es in den letzten paar tausend Jahren nicht so warm war wie gegenwärtig und daß dies ein Beleg für den menschlichen Einfluß auf die Temperatur sei.
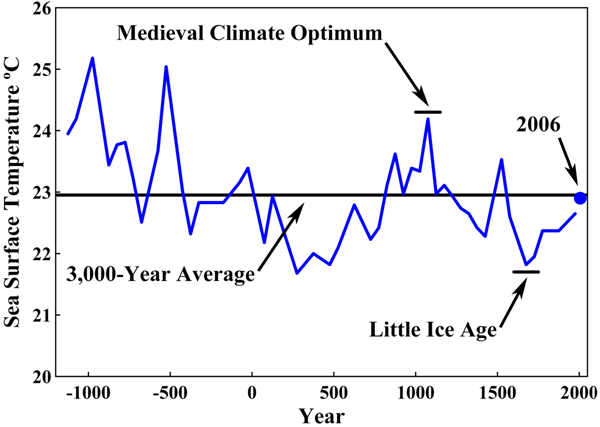
Aber im Hochmittelalter war es deutlich wärmer als jetzt.
-
JoNova
en Fraudulent hockey sticks and hidden data
These maps and graphs make it clear just how brazen the fraud of the Hockey Stick is.
It's clear that the world was warmer during medieval times.
Marked on the map are study after study (all peer-reviewed) from all around the world with results of temperatures from the medieval time compared to today.
These use ice cores, stalagmites, sediments, and isotopes.
They agree with 6,144 boreholes around the world which found that temperatures were about 0.5°C warmer world wide.
de Aus der Panik-Küche en From the panic laboratory fr De la marmite des alarmistes
-
2009-11-25 en
 Al Gore Lies about Melting Ice and Rising Sea Levels
Al Gore Lies about Melting Ice and Rising Sea Levels
↑
c) Die Kleine Eiszeit (von 1350 bis ca. 1850)
en The Little Ice Age
fr Petit âge glaciaire
- Die Kleine Eiszeit
- Die Kleine Eiszeit, eine frühneuzeitliche Klimakatastrophe
- 1816 The Year Without a Summer
- Kleine Eiszeit war global und extremste Kältephasen ereigneten sich zu Zeiten schwacher Sonnenaktivität
-
de
Die Kleine Eiszeit als weltweite Kältephase: Welche Rolle spielten
die Vulkane?
en From Schmidt 2005 to Miller 2012: the "not needed" excuse for omitted variable fraud - Videos
← Die Kleine Eiszeit / The Little Ice Age / Le petit âge glaciaire
-
de
Die Kleine Eiszeit war eine Periode relativ kühlen Klimas von Anfang
des 15. bis in das 19. Jahrhundert hinein.
Sie gilt in der heutigen Klimadiskussion als das klassische Beispiel einer durch kurzfristige Schwankungen geprägten natürlichen Klimavariation.
Doch auch während der Kleinen Eiszeit gab es erhebliche Klimaschwankungen. So stellen zum Beispiel die Zeiträume von 1570-1630 oder von 1675-1715 besonders kalte Zeitabschnitte dar.
-
en
The Little Ice Age (LIA) was a period of cooling occurring after
a warmer era known as the Medieval climate optimum.
It is generally agreed that there were three minima, beginning about 1650, about 1770, and 1850, each separated by slight warming intervals.
Any of several dates ranging over 400 years may indicate the beginning of the Little Ice Age:- 1250 for when Atlantic pack ice began to grow
- 1300 for when warm summers stopped being dependable in Northern Europe
- 1315 for the rains and Great Famine of 1315-1317
- 1550 for theorized beginning of worldwide glacial expansion
- 1650 for the first climatic minimum
-
fr
Le petit âge glaciaire (PAG) est une période climatique
froide survenue en Europe et en Amérique du Nord, d'environ
1550-1580 à 1850-1860.
Quelques grands évènements climatiques peuvent donc être soulignés comme des points de repère d'un petit âge glaciaire étendu du XIIIe siècle au milieu du XIXe siècle :- 1250 : début de l'extension de la calotte glaciaire en Atlantique
- 1300 : les étés jusqu'alors chauds cessent de l'être de façon nette
- 1315 : précipitations soutenues et Grande Famine de 1315-1317
- 1550 : début théorique de l'expansion mondiale des glaces
- 1650 : premier minimum climatique
Winterlandschaft des holländischen Malers Pieter Bruegel
des Älteren (1525-1569) aus dem Jahr 1565
und The frozen Thames, A. Hondius 1677 London Museum
-
Wikipedia de
Kleine Eiszeit
en Little Ice Age
fr Petit âge glaciaire
-
Wasserplanet de
Klimaänderungen der Vergangenheit
-
en/sous-titres fr:
 Video
Video
← Die Kleine Eiszeit, eine frühneuzeitliche Klimakatastrophe
-
NZZ
2004-01-24 de Die Kleine Eiszeit, eine frühneuzeitliche KlimakatastropheBemerkung:
Lesen Sie den Artikel bis zum Schluss, in dem die Frage gestellt wird, ob heute die Politiker, Umweltschützer, Geschäftsleute, Profiteure und Mitläufer mit der "Klimakatastrophe" die gleiche Hexenjagd auf CO2-Verursacher durchführen, wie dies im späten Mittelalter mit den "Schuldigen an der Eiszeit" geschehen ist.
-
Burghard Schmanck de Realsatire?
(Es soll auch an diejenigen gedacht werden, die selbst nachdenken und ihren Arbeitsplatz verlieren, wenn sie nicht die offizielle Auffassung vertreten)
| de | en | fr |
|---|---|---|
|
Klima-Diskurse: Diskussionen Ausschluss und Maulkorb für Kritiker |
Climate Discurses: Discussions Exclusion of critics |
Clima discurs: Discussions Exclusion des critiques |
← 1816 The Year Without a Summer
-
Watts Up With That? (Antoy Watts)
2009-06-20 en Historic Variation in Arctic Ice
The summer of 1816 was exceptionally cold (the year without a summer- probably due to the eruption of Mount Tambora in Indonesia on 10 April 1815)
The Hudson Bay ships bringing fur to London were actually frozen in during this period, whilst 1817 was an "Enso- el nino year" with the late winter of 1816 and summer of 1817 being warm, matching reports from earlier years that the ice was periodically melting, with a great deal of open water, and as reported by the Hudson bay co, and by others, as having an 'unprecedented break up' in 1815 and 1816.
In 1817 Scoresby contacted Banks about the melting,
In 1820 Scoresby found the ice around Greenland was melting and in 1822 mapped much of what had previously been an inhospitable coast.
-
Willie Soon and Steven H.Yaskell
en 1816 Year Without a Summer
1816 Year Without a Summer
A weak solar maximum, a major volcanic eruption, and possibly even the wobbling of the Sun conspired to make the summer of 1816 one of the most miserable ever recorded.
Du climat Lorrain 1312-1998
-
Skyfall / Changement Climatique
2007-06-25 fr Du climat Lorrain
Source:
-
TOUTE LA LORRAINE
fr Du climat Lorrain
L'histoire du climat en Lorraine de 1312 à nos jours : inondation à Metz et Nancy, canicule, température en hivers, crue de la Moselle et de la Meurthe et hauteur d'eau, tremblement de terre, intemperies.
← Kleine Eiszeit war global und extremste Kältephasen ereigneten sich zu Zeiten schwacher Sonnenaktivität
-
Die kalte Sonne (Fritz Vahrenholt & Sebastian Lüning)
2014-12-12 de Studie der University of Gloucestershire: Kleine Eiszeit war global und extremste Kältephasen ereigneten sich zu Zeiten schwacher Sonnenaktivität
↑
a) Die Kleine Eiszeit als weltweite Kältephase: Welche Rolle spielten
die Vulkane?
en From Schmidt 2005 to Miller 2012: the
"not needed" excuse for omitted variable fraud
-
Die kalte Sonne (Fritz Vahrenholt & Sebastian Lüning)
2012-05-19 de Die Kleine Eiszeit als weltweite Kältephase: Welche Rolle spielten die Vulkane?Noch vor einigen Jahren gab es doch wirklich Wissenschaftler, die die Kleine Eiszeit und Mittelalterliche Wärmeperiode als lokales nordatlantisches Phänomen kleinreden wollten.
Was heute im Rückblick unvorstellbar erscheint, wurde erschreckenderweise von einigen Forschern jahrelang als angeblicher "Konsens" in der Öffentlichkeit verbreitet.
Es war die Zeit als die Welt noch von der Hockey Stick Kurve genarrt wurde.
Der frischgebackene Doktor Michael Mann hatte die Kleine Eiszeit und die Mittelalterliche Wärmeperiode mithilfe statistisch fragwürdiger Methoden und fehlerhafter Daten kurzerhand zu einem klimatisch ereignislosen Strich ausgebügelt.
Auch in Deutschland gab es prominente Unterstützung für diese heute nicht mehr nachvollziehbare Denkweise.
So spielte Stefan Rahmstorf vom Potsdam-Institut für Klimafolgenforschung (PIK) 2007 die zahlreichen weltweiten Hinweise auf die Mittelalterliche Wärmeperiode und die Kleine Eiszeit in einem FAZ-Beitrag mit den Worten herunter:
"Dass lokal und regional wesentlich größere Klimaschwankungen auftreten als in der globalen Mitteltemperatur, ist für jeden Klimatologen klar [...]. Diese mitteln sich jedoch global heraus [...]."
Die Hockey Stick Kurve ist heute Geschichte, die beiden lange bekannten, natürlichen Klimaschwankungen der letzten 1000 Jahre wieder rehabilitiert.
In seinem faszinierenden Buch "The Hockey Stick Illusion" schildert Andrew Montford wie die Hockey Stick Kurve enttarnt wurde, die noch im 2001er IPCC Bericht sowie in Al Gores Klimafilm eine tragende Rolle gespielt hatte.
In den letzten Monaten haben weitere wissenschaftliche Arbeiten den globalen Charakter der Kleinen Eiszeit eindrucksvoll belegen können.
Das angebliche "nordatlantische Phänomen" wurde nun gleich von drei Wissenschaftlergruppen in der Antarktis nachgewiesen.
So untersuchte ein Forscherteam der Scripps Institution of Oceanography der University of California in San Diego um Anais Orsi die Temperaturdaten eines 300 m tiefen Bohrlochs im West Antarktischen Eisschild.
In der im Mai 2012 in den Geophysical Research Letters erschienenen Studie konnten die Wissenschaftler zeigen, dass die Temperaturen im Untersuchungsgebiet von 1400 bis 1800 etwa ein halbes Grad unter dem Temperaturdurchschnitt der vergangenen 100 Jahre lag.
Die kalifornischen Forscher bestätigten damit den globalen Charakter der Kleinen Eiszeit.
Das frühere Modell einer reinen Wärmeumverteilung auf der Erde, also einem energetischen Nullsummenspiel, halten Anais Orsi und seine Kollegen aufgrund ihrer neuen Ergebnisse für abwegig.
Die auch von Rahmstorf einst propagierte Klimaschaukel, bei der die Kälte in einem Gebiet durch Wärme in einem anderen Gebiet ausgeglichen würde, hat sich letztendlich nicht bestätigt.
Im Januar 2012 war bereits eine neue Studie vom antarktischen Ross Schelfeis im Fachmagazin Climate oft he Past Discussions erschienen.
Ein Forscherteam um Rachel Rhodes vom Antarctic Research Centre im neuseeländischen Wellington konnte auch für das Rossmeer die Kleine Eiszeit in eindrucksvoller Weise nachweisen. Während der Kleinen Eiszeit lagen die Temperaturen in der Region etwa 1,75°C unter denen von heute.
Welche Rolle spielen die Vulkane?
Da der Weltklimarat die Bedeutung dieser Studien jedoch noch immer eisern kleinredet und die Sonne in den IPCC-Klimamodellen eine nur zu vernachlässigende Klimawirkung besitzt, brauchte der der IPCC dringend Ersatz für die kollabierte Hockey Stick-Argumentation.
Eine nichtsolare Alternative musste dringend her, die die benötigte Kühlung verursacht haben soll.
Bei der Suche nach einer neuen klimatisch dämpfenden Wunderwaffe fiel die Wahl auf kühlende Asche von Vulkanen.
Ein weiterer wichtiger Gesichtspunkt ist, dass es bereits eine ganze Reihe von "Kleinen Eiszeiten" in den letzten 10.000 Jahren gegeben hat.
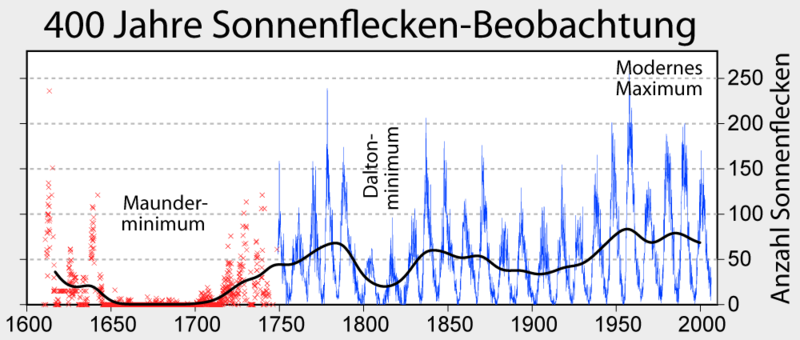
Immer wenn die Sonne im Verlauf ihres 1000-Jahreszyklus einen Tiefpunkt erreichte, gingen die Temperaturen zurück und es brach eine neue "Kleine Eiszeit" an.
Spinnt man die Vulkan-Idee zurück in der Zeit, müssten auch in all diesen Fällen "zufällig" immer Vulkane ausgebrochen sein, um dann die Kälteperiode zu erklären.
Könnte man das Absacken der Sonnenaktivität während der Kleinen Eiszeit im letzten Jahrtausend vielleicht gerade noch als Zufall durchgehen lassen, ist jedoch eine Vervielfachung dieses blöden Zufalls in den davorliegenden Jahrtausenden aus wissenschaftlicher Sicht vollkommen auszuschließen.
Das jahrtausendealte Muster spricht daher ganz eindeutig für einen solaren und weniger für einen vulkanischen Auslöser der Kleinen Eiszeit.
...
Die Kleine Eiszeit in Spanien, der Schweiz und Taiwan
...
-
Watts Up With That? (Antony Watts)
2012-04-29 en From Schmidt 2005 to Miller 2012: the "not needed" excuse for omitted variable fraudMiller et al. 2012 recently provided some pretty strong evidence for a solar driver of climate. "This is the first time anyone has clearly identified the specific onset of the cold times marking the start of the Little Ice Age," said lead author Gifford Miller in January. And the dates?
LIA summer cold and ice growth began abruptly between 1275 and 1300 AD, followed by a substantial intensification 1430-1455 AD.
As you can see in the graphic above (from Usoskin 2003) these dates correspond pretty much with the midpoints of the Wolf and Spörer solar minima.
(Usoskin 2007 centers Wolf at 1305 with a duration of 70 years and Spörer at 1470 with a duration of 160 years.)
Yet Miller never noted this coincidence.
In fact, he tried to hide it, claiming that the onset of snow and ice growth coincided with periods of especially high volcanism (debunked both by Willis and by Wired), while dismissing the solar explanation with a misleading reference to the Maunder Minimum:
...
← Videos
"All Things Cold"
-
9th International Conference on Climate Change 2014
2014-07-11 en Panel "All Things Cold" (2014 ICCC)
Panel "All Things Cold" (2014 ICCC)
Sonnenflecken und steigende Weizenpreise
en Sunspots and Rising Grain Prices
-
Watts Up With That? (Antony Watts)
David DuByne
2014-11-03 en 100 Year Snow Records broken across the South Eastern US on October
31st and November 01st
100 Year Snow Records broken across the South Eastern US on October
31st and November 01st
2014-10-02 en
 2015-2035 Mini Ice Age
(
Source)
2015-2035 Mini Ice Age
(
Source)
1 Sunspots and Rising Grain Prices
2 Snow and Record Cold 2014
3 Nine Arctic Seas Gain Ice 2014
4 Agricultural Losses 2014 from Cold Temperatures
Das neue solare Minimum hat begonnen. Kommt jetzt eine neue Kleine Eiszeit? Das folgende Video diskutiert, wie Chinas Landwirtschaftsstrategie aussehen könnte:
2015-03-23 en
![]() China's Food Production Strategy for the New Grand Solar Minimum
China's Food Production Strategy for the New Grand Solar Minimum
China's Food Production Strategy for the New Grand Solar Minimum.
What is their Knowledge of Solar Minimums and Climate Change since trading for 2000+ years to faraway destinations?
Do they know what the climate in Africa will change to this solar minimum and is why they are investing so heavily in N.Africa for future food production areas?
Land Grabbing
-
Wikipedia
de
Land Grabbing
en Land grabbing
fr Accaparement des terres
-
Basler Zeitung
2016-03-10 de Hier machte es bei Markus Ritter klickWissen Sie, was «Land Grabbing» bedeutet?
Für den obersten Schweizer Bauern war dies der Start für die Ernährungs-Initiative - wegen eines hohen Besuchs aus China.
Für den Bauernverbandspräsidenten ist klar, dass für die Versorgung der Schweizer Bevölkerung mit einheimischen Produkten viel Land gebraucht wird.
Die Schweiz sei jetzt nur noch zu 50 Prozent selbstversorgend, und es werde immer weniger.
Das chinesische Land Grabbing als Inspiration für die Initiative
Ritter vergleicht die Reduzierung von Kulturland in der Schweiz in seiner Argumentation mit dem Land Grabbing: dem grossflächigen Aufkaufen von Land in Schwellen- und Drittweltländern durch finanziell starke Staaten, vor allem in Afrika und in Asien.
«Das Land Grabbing zeigt, dass sich viele Staaten auf der ganzen Welt bewusst sind, dass die Versorgung ihrer Bevölkerung mittel- und langfristig mit dem eigenen Kulturland nicht gesichert ist», sagt Ritter.
In den kommenden 20 Jahren würde es in weiten Teilen der Erde zu einem «Engpass in der Ernährungssicherheit» kommen.
Es sei wichtig, dass die Versorgung der Schweizer Bevölkerung für die Zukunft gesichert werde: «Das geht nur, wenn der Verlust von Kulturland deutlich reduziert wird.
Andernfalls ist in 200 Jahren die ganze Schweiz vom Bodensee bis zum Genfersee verbaut.»
Besonders bekannt für das Land Grabbing sind die Chinesen. Schon seit mehreren Jahren kauft sich das Land systematisch in afrikanische Farmen, beispielsweise in Moçambique, ein und bringt zur Bewirtschaftung nicht selten gleich noch chinesische Bauern mit.
Es sind denn auch die Chinesen, die Ritter und die anderen Initianten für diese Initiative inspiriert haben.
Während eines Besuchs des chinesischen Ministerpräsidenten Li Keqiang, unter anderem auf einem Hof eines Mitglieds des Bauernverbands, sei die Idee entstanden, sagt Ritter.
Über 220 Millionen Hektaren wurden in Drittweltländern gekauft
Land Grabbing wird mittlerweile von vielen Staaten oder auch privaten Investoren getätigt. Japan, Südkorea und China bezwecken damit vor allem, sicherstellen zu können, ihre Bevölkerung ausreichend zu ernähren.
Golfstaaten wie Katar oder Saudiarabien haben das gleiche Ziel vor Augen, doch verschiedene Bedingungen.
Wegen der Wüstenlandschaften ist der landwirtschaftliche Anbau in ihren Ländern schwierig.
Durch den Ankauf von Land in fruchtbareren Regionen wollen sie vor allem unabhängiger werden.
Shocking Truth:Global Cooling, The Little Ice Age Begins in 2014
Little ICE Age - Big CHILL
-
en
 Little ICE Age - Big CHILL
Little ICE Age - Big CHILL
Little Ice Age: Big Chill reveals all traits of the Little Ice Age - its scientific properties, its natural causes, the people it affected and specific examples of areas it decimated.
-
Artikel über dieses Video
The History Channel presents:
en Little Ice Age: Big Chill
Little Ice Age: Big Chill
Zurück in die Eiszeit
In Search Of The Coming Ice Age
Original broadcast: May 1978.
de Die drohende Eiszeit der 1970er Jahre und die Klimahysterie der modernen Zeit.
en The coming ice age of the 1970s and the climte hysteria of modern times.
Global Cooling - The Coming Ice Age
-
2013-03-02 en
 The Coming Ice Age - 1978
The Coming Ice Age - 1978
-
2011-02-09 en
 1988 Documentary about the upcoming Ice Age
1988 Documentary about the upcoming Ice Age
-
2013-10-29 en
 New Little Ice Age Coming
New Little Ice Age Coming
Mike Lockwood about the prospects of a new LIA.
-
2013-05-19 en
 Ice Age of the dimming Sun in 30 years
Ice Age of the dimming Sun in 30 years
-
2009-10-25 en
 Professor George Kukla
Professor George Kukla
14 Temperature measurement and temperature records
Sea surface temperatures
- Petition Project: Sea Surface Temperature
Combined global land and marine surface temperature record from 1850 to 2006
- Climatic Research Unit: Global Temperature Record
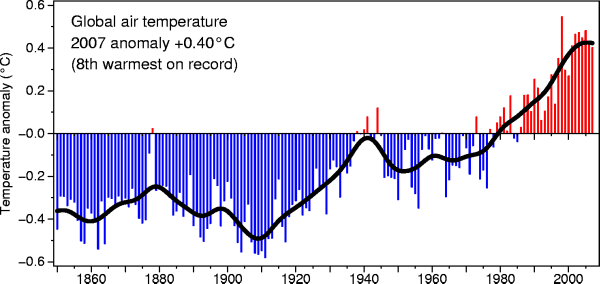
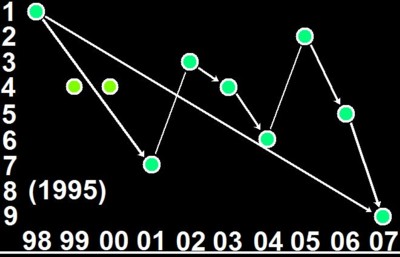
Global Cooling 1998-2008
Figure 1:
- Nine hottest years on record as shown by the RSS MSU calculations, from the hottest year 1998 to the coolest year 2007
Figure 2: Global cooling 2005-2007
- The trend is over 15 °C of cooling per century. ;-)
- Also, the trend is accelerating: for the 12 months of 2007, a similar linear regression gives about 35 °C of cooling per century. :-)
-
motls.blogspot.com
en 2007 Coldest in this century
15 Climate today
Das CO2 steigt und Temperaturen fallen
en CO2 is rising and
the temperature are falling
fr Le CO2 monte
et les températures baissent
- a de
Das CO2 steigt und die Temperaturen
fallen
en CO2 is rising and the temperatures are falling
fr Le CO2 monte et les températures baissent - b de
Die Abkühlung zeigt den IPCC-Irrtum: Es ist nicht das
CO2!
en The cooling shows the IPCC eror: It is not the CO2!
fr Le refroisissemen montre l'erreur du GIEC: Ce n'est pas le CO2! - c de
IPCC-Report 2007: Zeigt keine Abkühlung
en IPCC-Report 2007: Does not show the cooling
fr Rapport GIEC 2007: Ne montre pas le refroidissement - d de CO2-Ausstoß erreicht Rekordwerte während die Globaltemperatur fällt
- e de
Brief an Dr. Pachauri, IPCC (2008-04-14)
en Letter to Dr. Pachauri, IPCC
| de | en | fr |
|---|---|---|
| Neuste Informationen über den Klimawandel | News on Climate Change | Nouvelles informations sur le changement climatique |
| Die Erwärmungspause | The Hiatus | La pause du réchauffement climatique |
↑
a Das CO2 steigt und die Temperaturen fallen
en
CO2 is rising and the temperatures are falling
fr
Le CO2 monte et les températures baissent
↑
b Die Abkühlung zeigt den IPCC-Irrtum: Es ist nicht das
CO2!
en
The cooling shows the IPCC eror: It is not the
CO2!
fr
Le refroisissemen montre l'erreur du GIEC:
Ce n'est pas le CO2!
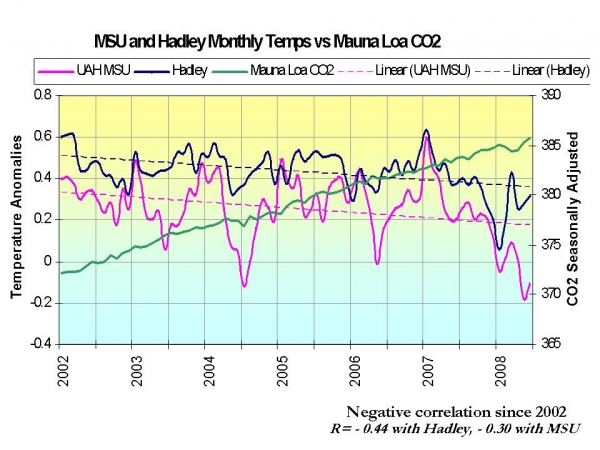
![]()
![]() World Temperatures Falling Whist CO2 Keeps Rising
World Temperatures Falling Whist CO2 Keeps Rising
-
EIKE Europäisches Komitee Für Klima und Energie Jena
2009-03-17 de Was man uns nicht erzählt! Die Warnungen von Experten vor einer unmittelbar bevorstehenden Klimakatastrophe sind ausschließlich das Produkt von Computermodellen
-
Research Review / Hans Labohm
2009-03 en What we are not being told
What we are not being told
-
CO2 Science COM
2008-10-28 en World Temperatures Falling Whist CO2 Keeps Rising
| de | Wenn das CO2 die Erwärmung erklärt, muss es auch die Abkühlung erklären ... oder es muss eine andere Erklärung gefunden werden, dass nebeneinander liegende kalte und warme Zonen - gleichzeitig - verschiedene Ursachen haben. |
| en | If the CO2 explains the warming, it must also explain the cooling ... or another explanation must be found how neighbor cold and warm sectors may - simultaneously - obey to different causes. |
| fr | Si le CO2 explique le réchauffement, il doit aussi expliquer le refroidissement ... ou bien une autre explication doit être trouvée, signifiant alors que des secteurs voisins, chauds et froids, peuvent - simultanément - obéir à des causes différentes. |
|
Marcel Leroux *1938-08-27 †2008-08-12 |
Professeur de climatologie PhD, Professor Emeritus of Climatology, University Jean Moulin of Lyon, France; former director of Laboratory of Climatology, Risks and Environment, CNRS ▶Marcel Leroux: Who is who (Skeptiker) ▶Marcel Leroux: Video (Präsentationen) ▶Marcel Leroux: Sites web (français) ▶Marcel Leroux: Wikipedia (Opfer von Wikipedia) |
![]()
![]() Temperature: HadCRUT3 (negative→positiv→negative),
CO2: Mauna Loa (positive)
Temperature: HadCRUT3 (negative→positiv→negative),
CO2: Mauna Loa (positive)
1939-2008

-
Global warming quiz by Dr. Richard Keen, University of Colorado, Boulder
Skyfall fr QCM sur le réchauffement climatique
↑
c IPCC-Report 2007: Zeigt keine Abkühlung
en
IPCC-Report 2007: Does not show the cooling
fr
Rapport GIEC 2007: Ne montre pas le refroidissement
-
de
Temperaturkurven - CRU 2007:
Die Abkühlung nach 2000 wird auf den Kurven des IPCC nicht gezeigt!
en Temperatures - CRU 2007:
The Cooling after 2000 is not showed on the IPCC diagrams!
fr Températures - CRU 2007:
Le refroidissement après 2000 n'est pas montré sur les diagrammes du GIEC!-
de
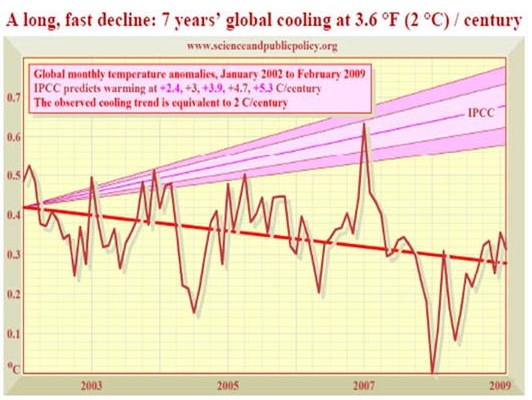
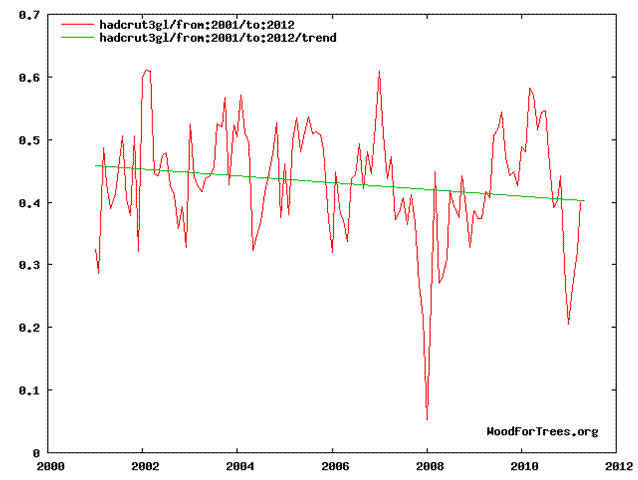
Deutliche Abkühlung nach 2000.
Diese Abkühlung kann mit dem CO2-Treibhauseffekt nicht erklärt werden.
en Visible cooling after 2000.
This cooling cannot be caused by the CO2 Greenhouse Effect.
fr Refroidissement apparente après 2000.
Ce refroidissement ne peut pas être expliqué avec l'effet de serre.
Quelle: / Source:
-
CRU - Climate Research Unit
UEA - School of Environmental Sciences University of East Anglia
en Home
en Temperature
en Global Temperature Record
-
de
Deutliche Abkühlung nach 2000.
-
de
IPCC Bericht 2007 zeigt keine Abkühlung nach 2000
en IPCC Report 2007 doesn't show the cooling after 2000
fr Rapport 2007 du GIEC ne montre pas le refroidissement après 2000-
de
Temperaturkurven - IPCC Rapport 2007:
Abkühlung nach 2000 wird nicht gezeigt!
Das IPCC kann diese Abkühlung nicht erklären.
Das IPCC irrt sich mit seiner Politik.
en Temperatures - IPCC Report 2007:
Cooling after 2000 is not showed!
IPCC cannot explain this cooling.
IPCC has to change his policy.
fr Températures - rapport GIEC 2007:
Le refroidissement après 2000 n'est pas montré!
Le GIEC n'a pas d'explication pour ce refroidissement.
Le GIEC doit modifier sa politique.
-
de
Temperaturkurven - IPCC Rapport 2007:
-
de
IPCC Temperatur Prognosen
en IPCC Temperature Prognnostics
fr Prévisions des températures du GIEC
- Source: IPCC/WG 1 Fig. 10.4
-
de
Die Prognosen sind nicht realistisch
Falsche Prognosen - Falsche Politik
en The prognostics are not realistic
Wrong prognostics - Wrong Politics
fr Le prognostiques ne sont pas réalistes
Fausses prognostiques - fausses politiques
↑ d CO2-Ausstoß erreicht Rekordwerte während die Globaltemperatur fällt
|
↑
e Brief an Dr. Pachauri, IPCC (2008-04-14)
en Letter to Dr. Pachauri, IPCC
fr Lettre adressée à Dr. Pachauri, GIEC
Dear Dr. Pachauri and others associated with IPCC
We are writing to you and others associated with the IPCC position
- that man's CO2 is a driver of global warming and climate change
- to ask that you now in view of the evidence retract support from the current IPCC position
and admit that there is no observational evidence in measured data going back 22,000 years or even millions of years that CO2 levels
(whether from man or nature) have driven or are driving world temperatures
or climate change.
...
de Wissenschaftler fordern IPCC zu Kurswechsel auf
-
In einem offenen Brief fordern Wissenschaftler und ein Friedensnobelpreisträger den Vorsitzenden des IPCC auf, die aktuellen Meßergebnisse zu akzeptieren, die auf eine Abkühlung während der letzten 10 Jahre hindeuten, oder aber Belege vorzulegen für die immer noch vom IPCC und anderen Vertretern der Treibhaushypothese vertretene Ansicht, es gebe eine Erwärmung und diese stehe mit dem CO2-Anteil der Atmosphäre in ursächlichem Zusammenhang.
Der Brief enthält auch Verweise auf öffentlich zugängliches Datenmaterial, das der CO2-Treibhaushypothese widerspricht.
en UN asked to admit climate change errors
- A group of four scientists has sent a letter to the UN's IPCC.
-
The Climate Scam
2008-04-14 de / en Wissenschaftler fordern IPCC zu Kurswechsel auf
-
The Climate Scam
2008-04-14 en UN asked to admit climate change errors
-
I love my carbondioxide
2008-04-14 en Dear Dr. Pachauri and others associated with IPCC
Dear Dr. Pachauri and others associated with IPCC
- Back en to Summary
- Full text en Sections 16 - 19